Turmeric Found to Be Beneficial for Lung, Liver and Colon Health
03/09/2016 / By trumericnews

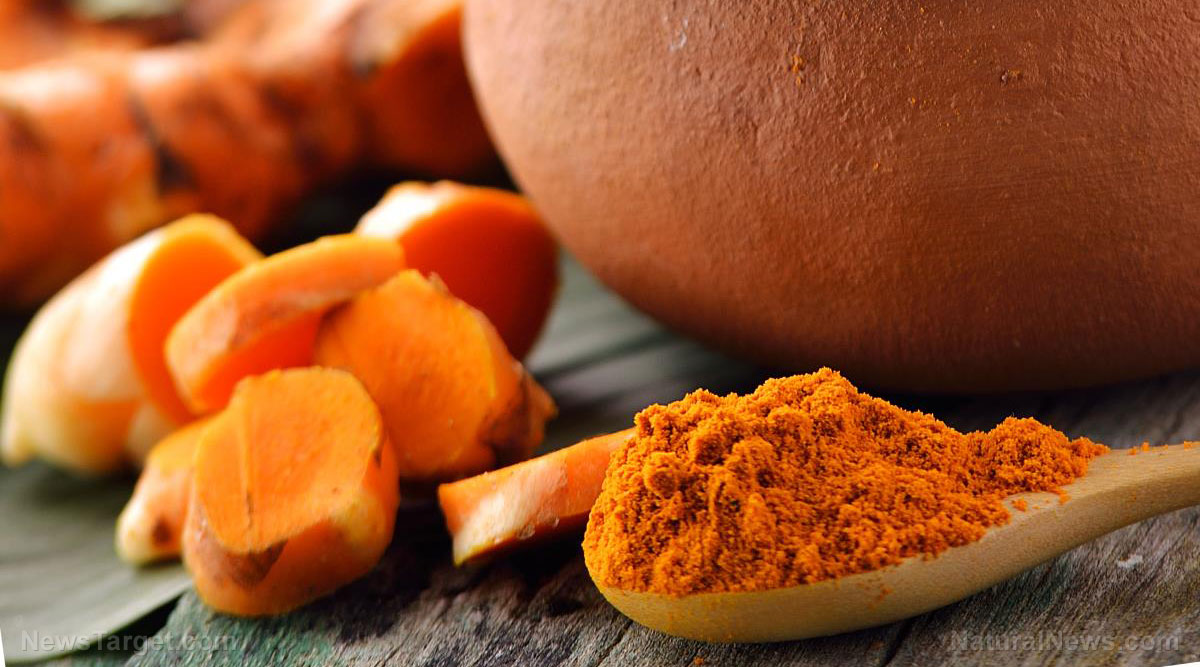
Turmeric, containing the active ingredient curcumin, is one of nature’s most powerful healers. The medicinal properties of this spice have slowly revealed themselves over the centuries. Turmeric is documented as effective in conditions ranging from cancer to Alzheimer’s disease. New research is now revealing its benefits as a preventative and treatment for lung, colon, and liver diseases.
Studies and Results – Lung Disease
In the 2007 Journal of Experimental Medicine and Biology researchers report that existing drugs have not been shown to be effective in the treatment of lung conditions resulting from occupational and environmental exposures to mineral dusts, airborne pollutants, cigarette smoke, chemotherapy, radiotherapy an other causes of acute and chronic inflammatory lung disease.
Several experimental animal models tested curcumin on lung fibrosis. Results demonstrated that curcumin attenuates lung injury and fibrosis caused by radiation, chemotherapeutic drugs, and toxicants. The researchers also note that studies support the conclusion that curcumin plays a protective role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute lung injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and allergic asthma. Its therapeutic action is on the prevention or modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress.
Molecular Nutritional and Food Research, March 2008, reports that corticosteroids have been one of the major modes of therapy against various chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, these corticosteroids have failed to be effective against these disease conditions because they don’t reduce the effects of oxidation.
Researchers reported that naturally occurring polyphenols in curcumin offer a safer alternative treatment. Curcumin can directly scavenge free radicals such as superoxide anion and nitric oxide, and modulate important signaling pathways. These polyphenols also down-regulate expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, and up-regulate desirable gene expression in the lungs. Researchers concluded that curcumin is a potential therapeutic agent against chronic lung diseases.
Colon disease
In the March edition of Molecular Nutritional Research, mice given an inflammatory agent that normally induces colitis were protected when curcumin was added to their diet five days beforehand. The mice receiving curcumin lost less weight than the control animals. When researchers checked their intestinal cell function, all the typical signs of colitis were greatly reduced. While the researchers are not yet sure exactly how curcumin achieves its protective effects, they think its benefits result from its antioxidant activity as well as its power to inhibit a major cellular inflammatory agent, NF kappa-B.
Another interesting feature of these results is that although curcumin has been found to be safe at very large doses, it was effective in this study at a concentration as low as 0.25 percent, an amount easily supplied by simply enjoying turmeric in your favorite dishes.
Liver disease
In the May 2008 edition of Langenbeck’s Archives of Surgery, researchers studied the effects of erythropoietin (a hormone that promotes formation of red blood cells) and granulocyte colony stimulating factor alone or in combination with curcumin, a liver protective antioxidant, in a model of delayed liver regeneration. Rats underwent a 70% liver resection and were grouped according to treatment following surgery.
Twenty four hours after surgery, blood and tissue samples were collected. Markers of liver regeneration, function, and hepatocellular damage were determined. Researchers concluded that erythropoietin alone did not improve liver regeneration. However, the combination of erythropoietin and curcumin resulted in highly significant stimulation of liver regeneration, which was accompanied by reduced oxidative stress.
What is turmeric?
Turmeric (curcuma longa) is the bright yellow of the spice rainbow, and is what gives curry its color. It was traditionally known as Indian saffron. Turmeric is also a powerful medicine that is one of the staples in Chinese and Indian healing. Oil of turmeric has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity in a variety of experimental models. The yellow or orange pigment of turmeric, called curcumin, is more potent than the oil, and is believed to be the primary pharmacological agent in turmeric.
Numerous studies have shown curcumin to be as potent against inflammation as hydrocortisone, phenylbutazone, and over the counter NSAID drugs like Motrin. Unlike these drugs, which are all associated with significant toxic effects, curcumin produces no toxicity.
Additional benefits of turmeric
Curcumin’s powerful antioxidant effects make it a popular, natural, therapeutic agent for diseases such as arthritis, where free radicals cause joint inflammation and eventual damage to the joints.
Epidemiological studies have linked frequent use of turmeric to lower rates of breast, prostate, lung, and colon cancer. Curcumin can prevent tumors from forming, and a recent study suggests that even when breast cancer is already present, curcumin can help slow the spread of breast cancer cells to the lungs.
Curcumin is able to do this by acting as a transcription factor, or a master switch. Transcription factors regulate all the genes needed for tumor formation. When they are switched off, the growth and invasion of cancer cells is halted.
Turmeric may prevent the oxidation of cholesterol in the body. It is oxidized cholesterol that damages blood vessels and builds up in the plaque that can lead to heart attack or stroke. Turmeric also contains vitamin B6 which is needed to keep homocysteine levels from getting too high. High homocysteine levels damage blood vessel walls and are considered a significant risk factor for blood vessel damage, atherosclerotic plaque build-up, and heart disease.
Evidence is mounting that turmeric may afford protection against neurodegenerative diseases through its ability to cross the blood brain barrier. Alzheimer’s disease is thought to occur when a fragmented protein accumulates in brain cells producing oxidative stress and inflammation, and forming plaque between nerve cells in the brain that disrupt function. Curcumin may prevent this oxidation and inflammation.
Using turmeric
Dried turmeric is widely available, but the best sources may be local spice stores or ethnic markets. Try to select organically grown turmeric since you will then know that it has not been irradiated. Color is not a criterion of quality. Turmeric has a much higher content of curcumin than does curry powder and can often successfully replace curry powder in recipes. Turmeric should be stored in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dark, dry place.
Wonderful recipes using turmeric can be found online. If you’re not into cooking, you can easily mix turmeric into rice. It is also a tasty addition to egg salad and brightens its color. If you are doing a cancer preventative version of the Budwig diet, see (http://www.naturalnews.com/022418.html) , you can mix a spoonful into your morning cottage cheese/flax oil combo, and maybe add in some cayenne too.
If you want to take the really easy way, you can buy Turmeric in capsule form, although this is the expensive way to do it. Nature’s Way makes the only readily available turmeric extract capsule that is free of magnesium stearate. Although the directions say 1 capsule up to 3 times per day, many natural healers recommend 3 capsules, 3 times a day when you begin, and then reducing the amount as your inflammation decreases.
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
health, Spices, Super foods, supplements, turmeric
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 TURMERIC NEWS